Atheist and anti-theist Jonathan M. S. Pearce’s “About” page states: “Pearce is a philosopher, author, blogger, public speaker and teacher from Hampshire in the UK. He specialises in philosophy of religion, but likes to turn his hand to science, psychology, politics and anything involved in investigating reality.” His words will be in blue.
*****
Jonathan wrote a paper called “On Harmonising Biblical Contradictions” (7-23-17). I replied with “Gadarenes, Gerasenes, Swine, & Atheist Skeptics” (7-25-17). He then counter-replied with “The Demons! The Demons! Replying to Armstrong on Biblical Contradictions” (7-29-17). This is my reply to the latter.
Problem 2 – one or two demons
Problem 2
I will start with Problem 2 because Dave appears not to have even read my original piece, deferring to the very argument I decry. . . .
The number of demons are multiple in all accounts (Mk 5:9-12; Mt 8:31; Lk 8:30-33), so that is a non-issue as well. Why, then, does Jonathan wonder about “one or two demons”? It’s neither. It is “many.”
Wow. Okay, so he starts out by attacking my logic, and then says that they all state many. But the passages are very explicit, as I quoted them:
[he then merely reposts the passages as he did in his first piece: Mark 5:1-2; Matthew 8:28; and Luke 8:26-27]
Note that at this point in the argument he is discussing how many demons were mentioned in these stories, not men (that comes later). He claims I didn’t even read his arguments, but I did, which is why I denied that the issue of either one or two men and one or more demons involves technical logical contradiction. Hence, in the larger citation of my words one can see how I included both:
The “one or two” [men / demons] supposed “contradiction” is clearly not one at all, by the rules of logic.
But (again) here at this point, following Jonathan’s own progression of argument, he mentioned only the numbers of demons. Readers will note that the passages I list, having to do with the incident, are from the latter parts of the accounts, where all mention multiple demons. That‘s what I was referring to. Mark 5:9 (RSV, as throughout) has the demons saying “we are many”. 5:12-13 add “they begged him” / “Send us . . . let us . . .” / “he gave them leave” / “unclean spirits”. So there are multiple demons involved, not one. Matthew 8:31 (and 8:32) are very similar, mentioning “demons” and using plural forms of words several times. Luke 8:30-33 is also the same, mentioning “many demons” and “the demons” etc.
This was my reply to “one or two demons.” Even that is an inaccurate way to describe the passage. The question is whether there was one demon or many. All three gospels fully agree that there were many. So Jonathan’s query as to supposed contradictoriness is literally nonsensical. There is no “problem” here. It may be, however, that Jonathan was mistakenly using the term “demons” to refer to the men. The proper term to use is “demoniacs” or “demon-possessed men.”
Then right after citing his three passages (needlessly, since I saw them already in his first piece), he goes right into the supposed “contradiction” of one or two men (depending on which Gospel report one reads):
Whether you like it or not, Jesus was either met by one man or two. I couldn’t give a withered fig as to whether this is remotely important or not, but it is a contradiction.
Once again, it is not a contradiction, and I explained why in what he already cited from me. He doesn’t seem to grasp it, so here it is again:
Mentioning one is as easily explained as saying that one writer drew from a (non-infallible) oral tradition in which one was mentioned, and the second from a tradition that mentioned two. Even those weren’t necessarily contradictory. In order to be, one account would have to say “only one” and the other “two.” That would be a logical contradiction. But they don’t . . .
This basic fact of the nature of a numerical contradiction remains true, no matter how much Jonathan prattles on about how folks ought to talk about numbers (“bastardisation of the English language” etc.). He also wastes much ink arguing with another apologist, J. P. Holding. He’s more than able to defend himself. I defend my own arguments, thank you.
But there are additional observations about this that may be helpful: having to do with emphasis. The Thy Word is True website (“Demoniacs: One or Two?”) gives a perfectly plausible explanation that I think Jonathan hasn’t considered (nor did I myself before I read it; but it makes perfect sense):
[I]n Matthew 8:28, it is giving an extra information, that there was a second demon-possessed person. One was the leader of the two. Of course, one of the two was possessed by “Legion”. Yet, it is also possible that these “legion” of demons possessed both of the unfortunate men. Whatever the case, the thing is that only one of the two demon-possessed men responded to Jesus Christ after He set them free from the demons and cast the demons into the group of swine.
[I will use RSV for the Bible citations in this quote]
Mark 5:18-19 And as he was getting into the boat, the man who had been possessed with demons begged him that he might be with him. [19] But he refused, and said to him, “Go home to your friends, and tell them how much the Lord has done for you, and how he has had mercy on you.”
Luke 8:38-39 The man from whom the demons had gone begged that he might be with him; but he sent him away, saying, [39] “Return to your home, and declare how much God has done for you.” And he went away, proclaiming throughout the whole city how much Jesus had done for him.
This is why only Mark and Luke mention only one demon-possessed person because only he was of significance to the story. Only he gave thanks to Jesus Christ our Lord for setting him free from Satan’s minions. The other was not mentioned because he probably gave no thanks to Jesus Christ and ran off still stuck in his evil ways. Now look at the man who did respond to Jesus Christ.
Luke 8:35 Then people went out to see what had happened, and they came to Jesus, and found the man from whom the demons had gone, sitting at the feet of Jesus, clothed and in his right mind; and they were afraid.
Matthew does not mention that this man expressed appreciation and a desire to follow and be with Jesus. So the key to the difference is “Mark and Luke mention only one demon-possessed person because only he was of significance to the story. Only he gave thanks to Jesus Christ . . .”
Gleason L. Archer, author of the wonderful (but to atheists, notorious and infamous) Encyclopedia of Bible Difficulties (Grand Rapids, Michigan: Zondervan, 1982) approaches the same question differently, but still similarly:
Mark and Luke center attention on the more prominent and outspoken of the two, the one whose demonic occupants called themselves “Legion.”
As a seminary professor I have occasionally had small elective courses containing only two students. In some cases i remember only one of them with any distinctness, simply because he was the more brilliant and articulate of the two. If I were to compose a set of memoirs and speak of only one of my two-student class, I could hardly be charged with contradicting the historical fact that there were actually two of them in the elective course. (p. 325).
Likewise, Mark and Luke don’t contradict the other two because they mention only one man anymore than a baseball player contradicts himself in reminiscing: “I distinctly remember a person who expressed extreme gratefulness when I gave them my autograph on opening day.” He may also mention scores of others who were also there getting his autograph or he may not. But in any event, it’s not a contradiction to mention one person only. It would be only if he said, “this person was the only one there that day getting my autograph.”
Luke takes the same approach in the story of the healing of blind Bartimaeus. Archer elaborates:
Matthew was concerned to mention all who were involved in this episode . . . Matthew is content to record that actual scene of healing, whereas Luke gives particular attention to the entire proceedings, from the moment that Bartimaeus first heard about Jesus’ arrival — a feature only cursorily suggested by Mark 10:46 — because he is interested in the beggar’s persistence in request before the cure was actually performed on him. As for the second blind beggar, neither Mark nor Luke find him significant enough to mention; presumably he was the more colorless personality of the two. (Ibid., p. 333)
Jonathan then moves onto the “Gadarene / Gerasene / Gergesene” issue. Here, he chose to ignore the subtlest and most detailed portions of my argument: mostly citing experts. Therefore, I’ll post it again (between the two sets of five asterisks) — repetition being a great teacher!:
*****
Here are the actual descriptions (RSV):
Mark 5:1 . . . the country of the Ger’asenes.
Luke 8:26 . . . the country of the Ger’asenes . . .
Matthew 8:28 . . . the country of the Gadarenes . . .
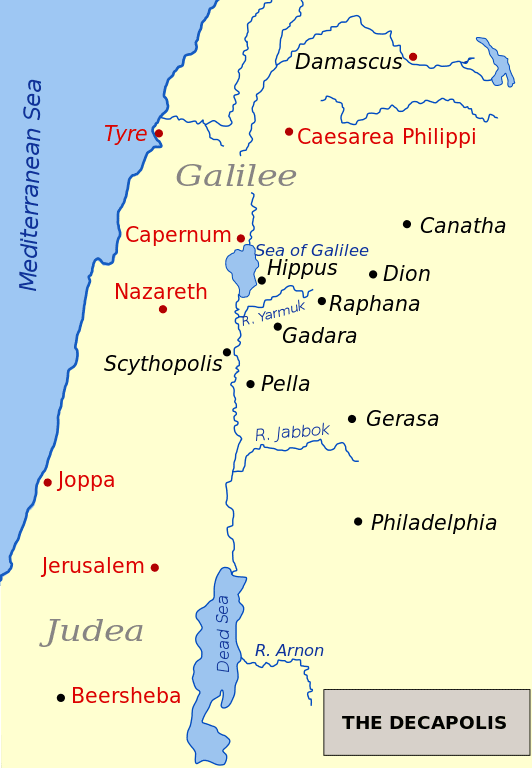
Note that the texts don’t say Gerasa or Gadara, so they aren’t necessarily referring just to one of the cities. They all say “country of . . .” (in the sense of region, not “nation”). “Gerasenes” could have had a sense of reference to the entire region (as well as to a city: just as “New Yorker” can refer to the state or city), and “Gadarenes” likely was a reference to the most prominent city of the region at the time. Smith’s Bible Dictionary provides what I find to be a quite plausible explanation (not “special pleading” at all), and analogous to how we still use place names today:
These three names are used indiscriminately to designate the place where Jesus healed two demoniacs. The first two are in the Authorized Version. (Matthew 8:28; Mark 5:1; Luke 8:26) In Gerasenes in place of Gadarenes. The miracle referred to took place, without doubt, near the town of Gergesa, the modern Kersa, close by the eastern shore of the Sea of Galilee, and hence in the country of Gergesenes. But as Gergesa was a small village, and little known, the evangelists, who wrote for more distant readers, spoke of the event as taking place in the country of the Gadarenes, so named from its largest city, Gadara; and this country included the country of the Gergesenes as a state includes a county. The Gerasenes were the people of the district of which Gerasa was the capital. This city was better known than Gadara or Gergesa; indeed in the Roman age no city of Palestine was better known. “It became one of the proudest cities of Syria.” It was situated some 30 miles southeast of Gadara, on the borders of Peraea and a little north of the river Jabbok. It is now called Jerash and is a deserted ruin. The district of the Gerasenes probably included that of the Gadarenes; so that the demoniac of Gergesa belonged to the country of the Gadarenes and also to that of the Gerasenes, as the same person may, with equal truth, be said to live in the city or the state, or in the United States. For those near by the local name would be used; but in writing to a distant people, as the Greeks and Romans, the more comprehensive and general name would be given.
The Biblical Training site (“Gerasenes”) elaborates:
The fact that Matthew places the healing of “Legion” in the “country of the Gadarenes” whereas Mark and Luke place it in the “country of the Gerasenes” may be harmonized on the historical grounds that geographical boundaries overlapped, and on the exegetical consideration that “country” embraced a wide area around the cities.
It’s simply alternate names for the same area: thus not contradictory at all. I think the coup de grâce is to look up the Greek word for “country” in these passages, to see what latitude of meaning it has. In all three instances the word is chōra (Strong’s word #5561). Thayer’s Greek Lexicon defines it as “the space lying between two places or limits . . . region or country.” The Sea of Galilee was clearly one of the limits.
In Luke 2:8 it is applied to the city of Bethlehem; in Acts 18:23 to Galatia and Phrygia. In Mark 1:5 it is used of “the land of Judaea” (KJV) and in Acts 10:39,to “land of the Jews” (KJV). In Acts 8:1 we have the “regions of Judaea and Samaria” (KJV), and in Acts 16:6, Galatia alone. Thus it is not always used of one specific country (nation), but rather, usually to regions or areas of either small (Bethlehem) or large (Judaea and Samaria) size, including regions surrounding large cities.
All of this sure seems perfectly consistent with calling the same area the “country” (chōra) of either the Gerasenes or the Gadarenes, after the two major cities.
*****
Maybe this time Jonathan will grapple with these portions. His blithely passing over all this material is a classic example of what I meant when I wrote on his blog two days ago:
I think what happened in 2017 is that I saw that you were not addressing my arguments in full, but rather, taking shots at a few carefully selected ones and ignoring the others. And so I must have decided (one makes such decisions when there are many possible topics to write about) not to reply further. It looks like you only addressed (at all) two of my four Christmas-related posts and blew off my papers on “Contradictory” Genealogies of Christ? and Bethlehem & Nazareth “Contradictions”.
Obviously, then, you selected what you would spend time on, just as I did. I do give you credit, on the other hand, for at least doing that, in light of the behavior of many of your cohorts like Seidensticker, Madison, Loftus et al, who absolutely refuse to engage, other than with insults. And you haven’t banned me. Kudos!
Just for good measure, I’ll add a bit more material that Jonathan can choose to either again ignore or actually address. Gleason Archer tackles this “problem”:
[I]t is entirely possible that the political control of this region was centered in Gadara as the capital city. Hence it would be called “the land of the Gadarenes.” . . . (Ibid., p. 325).
The site Evidence for Christianity focuses on the different intended audiences for the Synoptic Gospels:
On the eastern side of the Sea of Galilee (actually to the Southeast) there are two cities. One is Gadara. The other is Gerasa. Gadara is the chief Jewish city of the area, so the more Jewish-oriented Matthew naturally calls this the region of the Gadarenes. The principle Graeco-Roman city in the area known as the Decapolis, was Gerasa . . . The more Roman-oriented Mark and the more Greek-oriented Luke naturally call the region, Gerasa and tell us the demoniac came from the region of the Gerasenes. Both cities are to the Southeast of the Sea of Galilee. Gerasa is larger, but is farther from the Sea. It was the chief city of the area. Gadara was closer, but not as significant a city. There is no contradiction here. If someone lived in the city of Norwalk, California, a suburb of Los Angeles, some would say that the person lived in Norwalk. Others would say that he or she lived in Los Angeles. If speaking to someone from Europe, surely they would say Los Angeles, but if speaking to someone from LA county, they would say Norwalk. This is not contradiction. It is a different description of the same facts, adapted to the audience of the facts.
Apologetics Press basically concurs:
Matthew, Mark, and Luke were writing of the same general area. The Roman city Gerasa was a famous city that would have been familiar to a Gentile audience, but Gadara, as the capital city of the Roman province of Perea, was the chief of the ten cities in Decapolis . . ., so even those who lived in Gerasa could have been called Gadarenes. The stamp of a ship on Gadarene coins suggests that the region called Gadara probably extended to Galilee . . .
Logic & Light comes at it from a different (and fascinating) angle:
Dr. Timothy McGrew persuasively argues that “country of the Gerasenes” refers not to Gerasa, but to the town of Kursi (which was in the region of Gadara). [Alleged Historical Errors in the Gospels, published online, 2012, pg. 52-53] He makes this argument based on the fact that the original Aramaic names for Gerasa and Kursi would have been spelled very similarly if not identically. Therefore, the identification with Gerasa is potentially due to an early copyist mistake or misinterpretation of Kursi.
Dr. McGrew’s theory is strongly supported by the geography of Kursi and early church history. Kursi is on the eastern shore of the Sea of Galilee and has a steep hill that runs directly into the water . . .
In addition, the early church, through the 3rd century church father Origen, identified Kursi as the town in which this miracle occurred. Further, an early 5th century Christian monastery was built in Kursi and seems to have been located there to commemorate this event.
I think all these attempts to harmonize the seeming contradiction are plausible and respectable. Jonathan will likely disagree. But then it gets down to an extremely complex discussion of why and how people differ on relative plausibility. In any event, I think the language Jonathan uses in his second post on the topic towards Christians who may believe explanations like the above (“disingenuous” / “scenarios that are unbelievably unlikely”) is unwarranted. As always, I appeal to fair-minded readers, attempting to be rational and objective, to make up their own minds. Both sides have been presented here.
***
Photo credit: Map of the Decapolis; Nichalp (12-14-05) [Wikimedia Commons / Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.5 Generic license]
***













