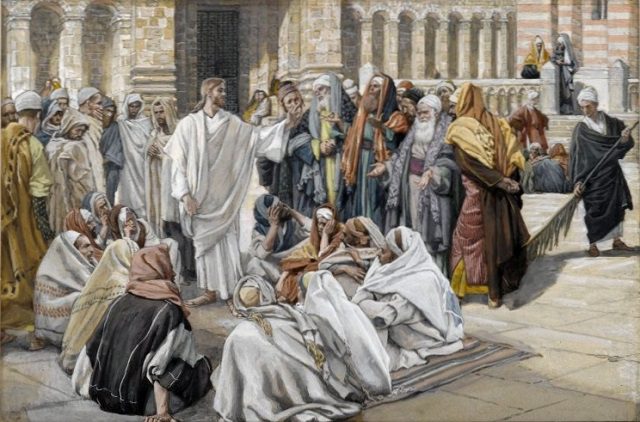
The Pharisees Question Jesus (1886-1894), by James Tissot (1836-1902) [public domain / Wikimedia Commons]
*****
(late 90s; rev. 8-16-16)
*****
Many Protestants (especially anti-Catholic ones) hold, by and large, the view that Scripture and sacred, apostolic tradition are somehow unalterably opposed to each other and, for all practical purposes, mutually exclusive. This is yet another example of a false dichotomy which Protestantism often (unfortunately) tends to create (e.g., faith vs. works, matter vs. spirit). The Bible, however, presupposes tradition as an entity prior to and larger than itself, from which it is derived, not as some sort of “dirty word.”
It is one thing to wrongly assert that Catholic tradition (the beliefs and dogmas which the Church claims to have preserved intact passed down from Christ and the apostles) is corrupt, excessive and unbiblical. It is quite another to think that the very concept of tradition is contrary to the outlook of the Bible and pure, essential Christianity. This is, broadly speaking, a popular and widespread variant of the distinctive Protestant viewpoint of sola Scriptura, or “Scripture Alone,” which was one of the rallying cries of the Protestant Revolt in the 16th century. It remains the supreme principle of authority, or “rule of faith” for evangelical Protestants today. Sola Scriptura by its very nature tends to pit tradition against the Bible.
First of all, one might also loosely define tradition as the authoritative and authentic Christian history of theological doctrines and devotional practices. Christianity, like Judaism before it, is fundamentally grounded in history: in the earth-shattering historical events in the life of Jesus Christ (the incarnation, miracles, crucifixion, resurrection, ascension, etc.). Eyewitnesses (Lk 1:1-2, Acts 1:1-3, 2 Pet 1:16-18) communicated these true stories to the first Christians, who in turn passed them on to other Christians (under the guidance of the Church’s authority) down through the ages. Therefore, Christian tradition, defined as authentic Church history, is unavoidable.
Many Protestants read the accounts of Jesus’ conflicts with the Pharisees and get the idea that He was utterly opposed to all tradition whatsoever. This is false. A close reading of passages such as Matthew 15:3-9 and Mark 7: 8-13 will reveal that He only condemned corrupt traditions of men, not tradition per se. He uses qualifying phrases like “your tradition,” “commandments of men,” “tradition of men,” as opposed to “the commandment of God.” St. Paul draws precisely the same contrast in Colossians 2:8: “See to it that no one makes a prey of you by philosophy and empty deceit, according to human tradition, according to the elemental spirits of the universe, and not according to Christ.”
The New Testament explicitly teaches that traditions can be either good (from God) or bad (from men, when against God’s true traditions). Corrupt pharisaic teachings were a bad tradition (but many of their legitimate teachings were recognized by Jesus; see, e.g., Matthew 23:3). The spoken gospel and the apostolic writings which eventually were formulated as Holy Scripture (authoritatively recognized by the Church in 397 A. D. at the council of Carthage) were altogether good: the authentic Christian tradition as revealed by the incarnate God to the apostles.
The Greek word for “tradition” in the New Testament is paradosis. It occurs in Colossians 2:8, and in the following three passages:
1 Corinthians 11:2 (RSV) . . . maintain the traditions even as I have delivered them to you. (NRSV, NEB, REB, NKJV, NASB all use “tradition[s]”).
2 Thessalonians 2:15 So then, brethren, stand firm and hold to the traditions which you were taught by us, either by word of mouth or by letter.
2 Thessalonians 3:6: Now we command you, brethren, in the name of our Lord Jesus Christ, that you keep away from any brother who is living in idleness and not in accord with the tradition that you received from us.
Note that St. Paul draws no qualitative distinction between written and oral tradition. He doesn’t regard oral Christian tradition as bad and undesirable. Rather, this false belief is, ironically, itself an unbiblical “tradition of men.”
When the first Christians went out and preached the Good News of Jesus Christ after Pentecost, this was an oral tradition proclaimed by “word of mouth.” Some of it got recorded in the Bible (e.g., in Acts 2) but most did not, and could not (see John 20:30; 21:25). It was primarily this oral Christian tradition that turned the world upside down, not the text of the New Testament (many if not most people couldn’t read then anyway). Accordingly, when the phrases “word of God” or “word of the Lord” occur in Acts and the epistles, they almost always refer to oral preaching, not to the written word of the Bible. A perusal of the context in each case will make this abundantly clear.
Furthermore, the related Greek words paradidomi and paralambano are usually rendered “delivered” and “received” respectively. St. Paul in particular repeatedly refers to this handing over of the Christian tradition:
1 Corinthians 15:1-3 Now I would remind you, brethren, in what terms I preached to you the gospel, which you received, in which you stand, [2] by which you are saved, if you hold it fast — unless you believed in vain. [3] For I delivered to you as of first importance what I also received, that Christ died for our sins in accordance with the scriptures,
1 Thessalonians 2:13 And we also thank God constantly for this, that when you received the word of God which you heard from us, you accepted it not as the word of men but as what it really is, the word of God, which is at work in you believers.
Jude 3 . . . contend for the faith which was once for all delivered to the saints.
(cf. Lk 1:1-2; Rom 6:17; 1 Cor 11:23; Gal 1:9, 12; 2 Pet 2:21)
Far from distinguishing tradition from the gospel, as evangelicals often contend, the Bible equates tradition with the gospel and other terms such as “word of God,” “doctrine,” “holy commandment,” “faith,” and “things believed among us.” All are “delivered” and “received”:
1) Traditions “delivered” (1 Cor 11:2), “taught . . . by word of mouth or by letter” (2 Thes 2:15), and “received” (2 Thes 3:6).
2) The Gospel “preached” and “received” (1 Cor 15:1-2; Gal 1:9, 12; 1 Thes 2:9).
3) Word of God “heard” and “received” (Acts 8:14; 1 Thes 2:13).
4) Doctrine “delivered” (Rom 6:17; cf. Acts 2:42).
5) Holy Commandment “delivered” (2 Pet 2:21; cf. Mt 15:3-9; Mk 7:8-13).
6) The Faith “delivered” (Jude 3).
7) “. . . things which have been accomplished among us” were “delivered” (Lk 1:1-2).
Clearly, all these concepts are synonymous in Scripture, and all are predominantly oral. In St. Paul’s writing alone we find four of these expressions used interchangeably. And in just the two Thessalonian epistles, “gospel,” “word of God,” and “tradition” are regarded as referring to the same thing. Thus, we must unavoidably conclude that “tradition” is not a dirty word in the Bible. Or, if one insists on maintaining that it is, then “gospel” and “word of God” are also bad words! Scripture allows no other conclusion: the exegetical evidence is simply too plain.
To conclude our biblical survey, we again cite St. Paul and his stress on the central importance of oral tradition:
2 Timothy 1:13-14 Follow the pattern of the sound words which you have heard from me, in the faith and love which are in Christ Jesus;
[14] guard the truth that has been entrusted to you by the Holy Spirit who dwells within us.2 Timothy 2:2 and what you have heard from me before many witnesses entrust to faithful men who will be able to teach others also.
St. Paul is here urging Timothy not only to “follow the pattern” of his oral teaching “heard from me,” but to also pass it on to others. Thus we find a clear picture of some sort of authentic historical continuity of Christian doctrine. This is precisely what the Catholic Church calls tradition, or, when emphasizing the teaching authority of bishops in the Church, “apostolic succession.” The phrase “deposit of faith” is also used when describing the original gospel teaching as handed over or delivered to the apostles (see, e.g., Acts 2:42; Jude 3).
The Catholic Church considers itself merely the custodian or guardian of this revelation from God. The New Testament itself is a written encapsulation of primitive, apostolic Christianity: the authoritative and inspired written revelation of God’s new covenant. It is a development, so to speak, of both the Old Testament and early oral Christian preaching and teaching (i.e., tradition). The process of canonization of the New Testament took over 300 years and involved taking into account human opinions and traditions as to which books were believed to be Scripture.
Thus, the Bible cannot be separated and isolated from tradition and a developmental process. Christianity does not take the view of Islam, whose written revelation, the Q’uran, simply came down from heaven from Allah to Mohammad, without involving human participation in the least. Some extreme, fundamentalist forms of sola Scriptura have a very similar outlook, but these fail the test of Scripture itself, like all the other manifestations of the “Bible Alone” mentality. As we have seen, Scripture does not nullify or anathematize Christian tradition, which is larger and more all-encompassing than itself; quite the contrary.
In Catholicism, Scripture and tradition are intrinsically interwoven. They have been described as “twin fonts of the one divine well-spring” (i.e., revelation), and cannot be separated, any more than can two wings of a bird.
*****
Meta Description: Explanation of the Catholic notion of apostolic, sacred tradition, which is always harmonious with Holy Scripture.
Meta Keywords: Bible & Tradition, Bible Only, kerygma, oral proclamation, oral teaching, oral tradition, Preaching, Rule of Faith, sacred tradition, Scripture Alone, Sola Scriptura